To understand inflammation, it’s important to know the two different types—acute and chronic.
Acute inflammation is a normal and beneficial inflammatory response that is a vital part of the immune system. It helps protect, heal, and repair the body after injury, and defend it against foreign invaders like viruses and bacteria.For example, when harmful bacteria enter the body, or when we cut ourselves or sprain an ankle, the body’s defence system kicks in and initiates the heat and swelling we often feel from inflammation to help repair the damaged area and start the healing process.

Chronic inflammation is an abnormal inflammatory response that occurs over the long-term, and that brings about a steady, low level of inflammation. This type of inflammation can be triggered even when there are no invaders to fight or injury to heal. At times it can even fight our own healthy tissues and cells (i.e. autoimmune disorders).
Over time, chronic inflammation can lead to the breakdown of our arteries and organs, leading to other chronic diseases. Even though some foods and dietary habits play a significant role in promoting a negative inflammatory response, food and nutrition also have the power to help fight unwanted oxidative stress (through antioxidants) that can lead to inflammation in the body.
Below are the top 10 anti-inflammatory foods that help in a big way.
1. BLUEBERRIES (anthocyanins & quercetin)
 While all berries can help combat inflammation, blueberries pack the greatest antioxidant punch. One study found that in comparison to strawberries and blackberries, blueberries not only had the most antioxidants, but also the greatest variety of antioxidants, thus providing a wider range of anti-inflammatory protection. This can be attributed to the abundance of anthocyanins and quercetin (plant pigments in the flavonoid family) that act as powerful antioxidants protecting the body from the oxidative damage that can lead to inflammation.
While all berries can help combat inflammation, blueberries pack the greatest antioxidant punch. One study found that in comparison to strawberries and blackberries, blueberries not only had the most antioxidants, but also the greatest variety of antioxidants, thus providing a wider range of anti-inflammatory protection. This can be attributed to the abundance of anthocyanins and quercetin (plant pigments in the flavonoid family) that act as powerful antioxidants protecting the body from the oxidative damage that can lead to inflammation.
2. SWEET AND TART CHERRIES (anthocyanins & polyphenols)
Tart cherries tend to get all the inflammation-fighting credit, however studies have found that the consumption of either cherries can help prevent or decrease oxidative stress and inflammation. The cherry’s secret weapons include inflammation-fighting anthocyanins, polyphenols and vitamin C.
3. PINEAPPLE (bromelain)
Pineapple contains the special digestive enzyme bromelain, which has been shown to play a significant role as an anti-inflammatory agent in various conditions including bronchitis, sinusitis, arthritis and general inflammation. Bromelain also increases the absorption of the powerful antioxidant quercetin found in blueberries. So not a bad idea to sip on a pineapple-blueberry smoothie from time to time.
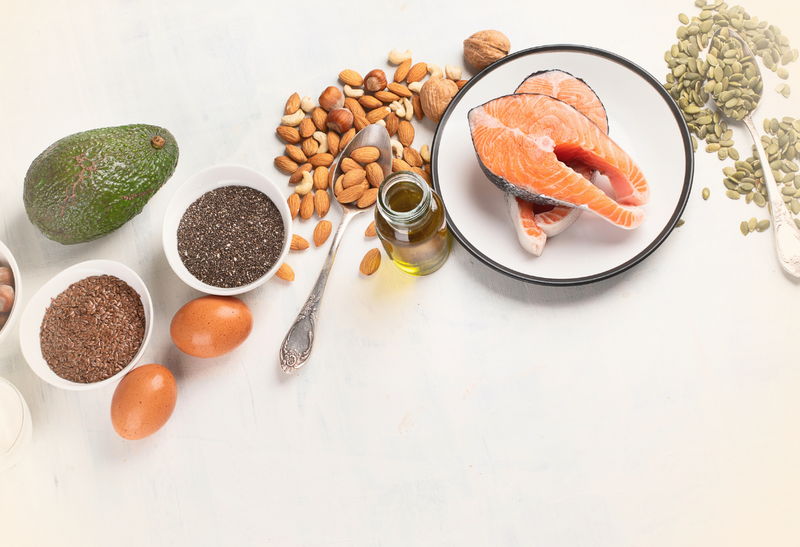
 4. WILD FATTY FISH OR ALGAE (omega-3s)
4. WILD FATTY FISH OR ALGAE (omega-3s)
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is the main compound in green tea, providing the body with an array of anti-inflammatory benefits. EGCG helps to suppress inflammatory cytokines and inflammation-related enzymes that can cause damage to our cells. And if you want to get the most antioxidants out of your green tea try matcha green tea, which uses the whole green tea leaf, packing in more antioxidants like EGCG. So, next time you see the trendy matcha latte at a cafe, you can rest assured it’s worth the health-promoting hype.
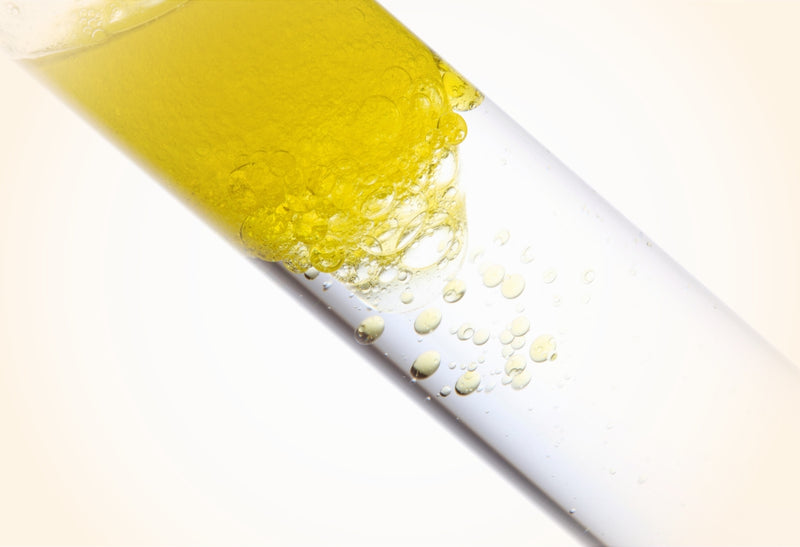
5. EXTRA VIRGIN OLIVE OIL (oleocanthal)
Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) has always gotten praise for contributing to the numerous anti-inflammatory benefits of the Mediterranean Diet. Researchers have discovered that most of this praise should go to a specific compound in EVOO called oleocanthal. Oleocanthal’s anti-inflammatory benefits are so strong they have been found to mimic the anti-inflammatory action of Ibuprofen!
6. AVOCADOS (monounsaturated fats & antioxidants)
 Avocados not only have the highest fruit lipophilic (“fat-loving”) antioxidant capacity but are also one of the few foods that contain significant levels of both vitamins C and E, which help protect the body from oxidation. They also contain significant amounts of lutein and zeaxanthin, carotenoids that support eye health.
Avocados not only have the highest fruit lipophilic (“fat-loving”) antioxidant capacity but are also one of the few foods that contain significant levels of both vitamins C and E, which help protect the body from oxidation. They also contain significant amounts of lutein and zeaxanthin, carotenoids that support eye health.
Avocados contain 185μg of lutein/zeaxanthin per one-half fruit, which is expected to be more highly bioavailable than most other fruit and vegetable sources. They also help to improve carotenoid absorption from other fruits and vegetables.
7. CRUCIFEROUS VEGETABLES (sulforaphane)
Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, and bok choy contain their own inflammation-fighting secret weapon, sulforaphane. Sulforaphane is a phytochemical beneficial compound in plants that has been shown to reduce inflammatory levels in the body, supporting a multitude of health conditions.
8. DARK LEAFY GREENS (antioxidants and polyphenols)
Dark leafy greens like kale, spinach, arugula, chard, collards, and microgreens are high in natural antioxidants and polyphenols—protective compounds found in plants. They are rich in vitamin K which provides a number of health benefits, including protecting your bones, supporting cognitive health, and supporting a positive inflammatory process.
9. TURMERIC (curcumin)
Most people associate turmeric root/spice with anti-inflammatory effects; however, its nutrient curcumin deserves all the credit. Unfortunately, absorbing enough curcumin from turmeric alone is difficult. Research shows that taking a daily curcumin supplement with better absorption mechanisms may be the best option for receiving the health benefits of curcumin.
 10. GREEN TEA (EGCG)
10. GREEN TEA (EGCG)
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is the main compound in green tea, providing the body with an array of anti-inflammatory benefits. EGCG helps to suppress inflammatory cytokines and inflammation-related enzymes that can cause damage to our cells. And if you want to get the most antioxidants out of your green tea try matcha green tea, which uses the whole green tea leaf, packing in more antioxidants like EGCG. So, next time you see the trendy matcha latte at a cafe, you can rest assured it’s worth the health-promoting hype.
TAKEAWAY
Avoiding a negative inflammatory response is critical to your overall health and the prevention of disease. Combat unwanted oxidative stress and inflammation on the body by incorporating some of these antioxidant-rich foods into your daily routine.